Vue状态管理
一、前端状态管理
前端状态管理解决的问题
- 方便组件通信(组件层层嵌套,单靠props等通信方式传递非常麻烦)
- 全局状态管理(比如登录情况下用户信息需全局获取)
- 状态持久化(页面刷新不持久)
为什么需要状态管理
提到概念单向数据流
二、Vuex
vuex的使用
集中式存储管理应用所有组件的状态。Vuex核心包括:state、getters、mutations、actions、mudules
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export const store = ({
state(){
return{ count:0 }
},
mutations:{
increment(state){
state.count++
}
},
actions:{
incrementActions(context){
context.commit('increment')
}
}
})
//main.js:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import { store } from './store'
const app = createApp(App).mount('#app')
app.use(store)
//组件中使用:
store.commit('increment')//调用mutations
store.dispatch('incrementActions')//调用actions
<template>
<div>
🧡{{$store.state.count}}
💛{{countAlias}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default{
computed:mapState({
count:state => state.count,//🧡
count:'countAlias',//💛重新命名
count(state){
return state.count + 1//💚需要使用依赖仓库值计算
}
})
//另一种写法,mapState完成了仓库与本地组件数据的映射:
computed:{ ...mapState['xxx']}
}
</script>
//可以将getters理解为全局的computed. store中定义:
{
state:{users:{
{id:1,name:'jery',gender:'male'},
{id:2,name:'mary',gender:'female'},
}},
getters:{
maleLength(state){
return state.users.filter(i => i.gender === 'male').length
}
}
}
//使用getters:
{{$store.getters.maleLength}}//方法一
{{maleLength}}
computed:{...mapGetters(['maleLength'])}//方法二
{{newMaleLength}}
computed:{...mapGetters({'maleLength':'newMaleLength'})}//重新命名
//mutations是vuex中的操作唯一能改变state状态的函数
//且必须是同步函数(vue为了更方便的去跟踪数据状态的变化)
this.$store.state.count++ //error
this.$store.commit('xxx') //right
//使用,如何传参
mutations:{
increment(state,payload){
state.count += paload.newValue
}
}
this.$store.commit('xxx',{ newValue1,newValue2,... })
//mapMutations用在methods中
methods:{...mapMutations['increment']}
//actions主要用来做异步操作,mutations是同步
mutations:{ increment(state){...} }
actions:{
incrementAction(context){
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment')
},1000)
}
}
//模板中使用actions:
this.$store.dispatch('incrementAction')//方法一
methods:{ ...mapActions['incrementAction'] }//方法二
methods:{ ...mapActions({'incrementAction':'newName'}) }//重新命名
//定义:
{
modules:{
users:{ state:{...},mutations:{...} },
foods: { state:{...},mutations:{...} },
}
}
//访问:工作中不建议使用,定义太复杂;这里涉及到命名空间的概念
this.$store.state.user
vuex的实现原理
Vuex 为 Vue Components 建立起了完整的生态圈,包括 API 调用的一环。围绕这个生态圈,总结下各模块在核心流程中的主要功能:
- Vue Components:即 Vue组件。HTML交互页面上,负责接受用户操作等交互行为,执行 dispatch 方法触发对应的 action 进行回应。
- dispatch:操作行为触发方法,唯一能执行 action 的方法。
- actions:操作行为处理模块,负责 Vue Components 接收的所有交互行为。包含同步、异步操作,支持多个同名方法,按照注册顺序依次触发。向后台 API 请求的操作就在这个模块中进行,包括触发其他 actions 以及提交 mutation 的操作。该模块提供了 Promise 封装,以支持 action 的链式触发。
- commit:状态改变提交操作的方法。对 mutation 进行提交,是唯一能执行 mutation 的方法。
- mutations:状态改变的操作方法。是 Vue 中唯一能修改 state 的方法。此方法只能同步操作,方法名需全局统一。操作中会有一些 hook 暴露出来,以进行对 state 的监控。
- state:页面状态管理容器对象。集中储存 Vue Components 中 data 对象的零散数据,全局唯一,以进行统一的状态管理。页面显示所需数据从该对象中进行读取,利用 Vue 的细粒度数据响应机制来进行高效的状态更新。
- getters:state 对象的读取方法,Vue Components 通过此读取全局 state 对象。
三、Pinia
- state、getters、actions
- pinia 没有命名空间
- pinia 是平面的数据结构(无需和vuex一样有规定写法 比如必须放在state中等),
可以任意交叉组合(相互访问store中的数据)
pinia的使用
- 安装
yarn add pinia --save
- 使用(main.js)
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
app.use(createPinia())
- 定义状态库(store.js)
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
//定义名字最好用use开头,因为返回值是一个hooks
//defineStore的第一个参数是id名称,必须确保这是全局唯一的,原理部分会说明为什么
export const useOptionsStore = defineStore('optionStore',{
state:() => {
return{ count:0 }
},
getters:{
getCount:(state) => {
return state.count
}
},
actions:{
setCount:(newCount) => {
state.count = newCount
}
}
})
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { ref,computed } from 'vue'
export const useSetupStore = defineStore('setupStore',() => {//与选项式不同,第二个参数是函数
const countRef = ref(0)
//ref,vue3中自定义解析和引用组件的API,允许在组件内使用ref引用组件实例,无需通过setup手动创建
const getCount = computed(() => {
return countRef
})
const setCount = (newCount) => {
countRef.value = newCount
}
return { countRef,getCount,setCount }
})
- 使用
import { useSetupStore } from '...'//每次使用都要引入 和vuex中的全局$store不一样
const counter = useSetupStore()
//必须是函数调用的方式,如上 组合式定义中,useSetupStore是一个函数,调用的结果就是return中的🤎
counter.count++ //方法一
counter.setCount(1) //方法二
counter.$dispatch({count:counter.count + 1}) //方法三 pinia提供的
counter.$reset()//pinia提供的重置方式
pinia的原理
- 思路第1步:先看pinia的引入
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
app.use(createPinia())
//app.use是挂载插件,即将createPinia看成插件,去执行它身上的install方法(这是vue插件决定的📌)
//接下来就去看 createPinia 做了什么事情
思路第2步:install方法中,app.provide方法提供了一个pinia全局对象;创建了scope和state并挂载到pinia身上📌
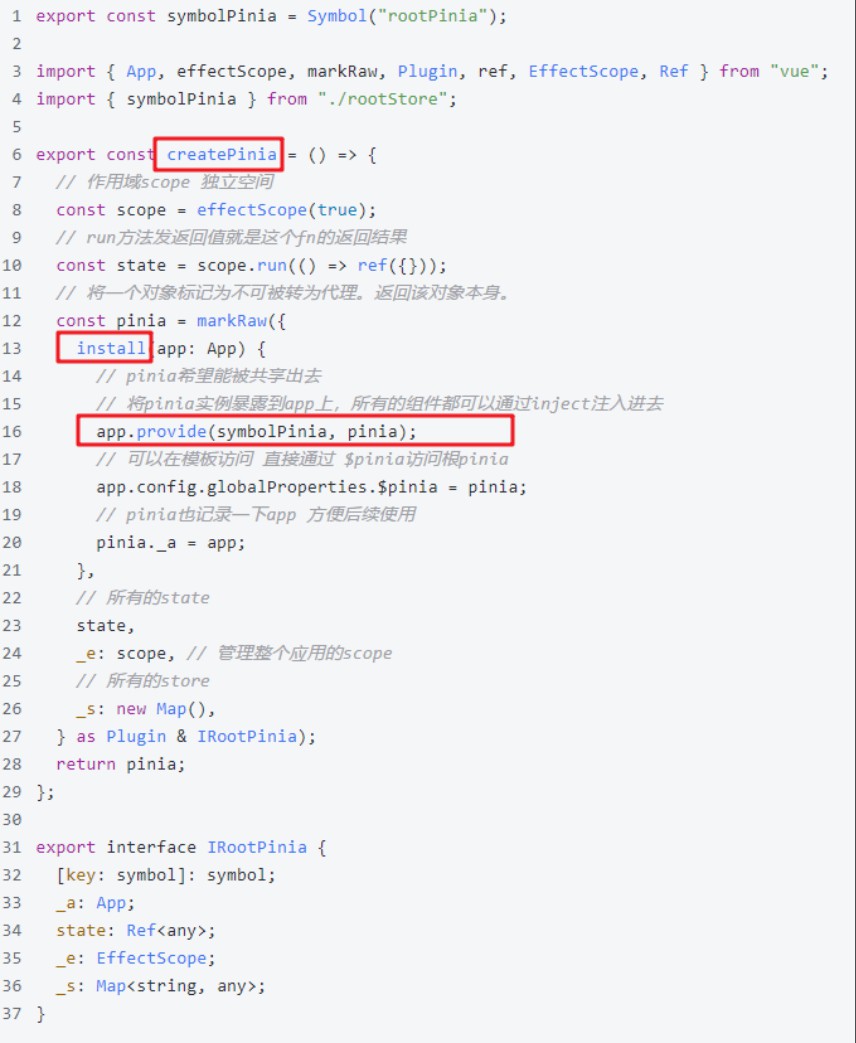
思路第3步:看pinia的使用中,defineStore做了什么(pinia中state的实现)
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useSetupStore = defineStore('id',() => {})
import {
getCurrentInstance,
inject,
effectScope,
EffectScope,
reactive,
} from "vue";
import { IRootPinia } from "./createPinia";
import { symbolPinia } from "./rootStore";
export function defineStore(options: IPiniaStoreOptions): any;
export function defineStore(
id: string,
options: Pick<IPiniaStoreOptions, "actions" | "getters" | "state">
): any;
export function defineStore(id: string, setup: () => any): any;
export function defineStore(idOrOptions: any, storeSetup?: any) {
let id: string, options: any;
if (typeof idOrOptions === "string") {
id = idOrOptions;
options = storeSetup;
} else {
// 这里就是一个参数的形式 id参数定义在对象内
options = idOrOptions;
id = idOrOptions.id;
}
// 注册一个store
function useStore() {
// 必须在setup中使用
const currentInstance = getCurrentInstance();// 获取组件实例
if (!currentInstance) throw new Error("pinia 需要在setup函数中使用");
// 注入 pinia
const pinia = inject<IRootPinia>(symbolPinia)!;//这里的inject与将思路第2步中的provide对应📌
// 还没注册
if (!pinia._s.has(id)) {
// counter:state:{count:0}
createOptionsStore(id, options, pinia);
}
// 获取store
const store = pinia._s.get(id);
//_s是在思路第2步中new Map()一个空对象,即用于做存储的 => 再去找如何存储思路📌createOptionsStore
return store;
}
return useStore;//这里return的是个函数,本文章中搜索🤎的源码说明处
}
const createOptionsStore = (
id: string,
options: Pick<IPiniaStoreOptions, "actions" | "getters" | "state">,
pinia: IRootPinia
) => {
const { state, getters, actions } = options;//获取defineStore中对象式定义的值
// store单独的scope
let scope: EffectScope;
const setup = () => {
// 缓存 state
if (pinia.state.value[id]) {
console.warn(`${id} store 已经存在!`);
}
const localState = (pinia.state.value[id] = state ? state() : {});
//注意这里有个判断 为state()函数调用,在选项式定义状态库中 state要return出去的原因
return localState;
};
// scope可以停止所有的store 每个store也可以停止自己的
const setupStore = pinia._e.run(() => {
scope = effectScope();
//effectScope返回的setup函数,收集响应过程中产生副作用的集中统一管理,如销毁状态
//vue3官网可以搜到,日常开发不会用到,写插件可能会用到📌
return scope.run(() => setup());
});
// 一个store 就是一个reactive对象
const store = reactive({});
Object.assign(store, setupStore);//通过Object.assign将所有对象都变成响应式
// 向pinia中放入store
pinia._s.set(id, store);
console.log(pinia)
};
export interface IPiniaStoreOptions {
id?: string;
state?: () => any;
getters?: any;
actions?: any;
}
- 思路第4步:看pinia的使用中,defineStore做了什么(actions和getters的实现)
const createOptionsStore = (
id: string,
options: Pick<IPiniaStoreOptions, "actions" | "getters" | "state">,
pinia: IRootPinia
) => {
const { state, getters = {}, actions } = options;
// store单独的scope
let scope: EffectScope;
const setup = () => {
// 缓存 state
if (pinia.state.value[id]) {
console.warn(`${id} store 已经存在!`);
}
const localState = (pinia.state.value[id] = state ? state() : {});
return Object.assign(
localState,
actions,//actions的核心是用了Object.assign方法,将state、getters、actions合并成了对象📌
Object.keys(getters).reduce(
(computedGetter: { [key: string]: ComputedRef<any> }, name) => {
// 计算属性可缓存
computedGetter[name] = computed(() => {
//getters的核心就是用computed包了一层,监测getters的变化📌
return Reflect.apply(getters[name], store, [store]);
// 我们需要获取当前的store是谁
});
return computedGetter;
},
{}
)
);
};
// scope可以停止所有的store 每个store也可以停止自己的
const setupStore = pinia._e.run(() => {
scope = effectScope();
return scope.run(() => setup());
});
// 一个store 就是一个reactive对象
const store = reactive({});
// 处理action的this问题
for (const key in setupStore) {
const prop = setupStore[key];
if (typeof prop === "function") {
// 扩展action
setupStore[key] = wrapAction(key, prop, store);
}
}
Object.assign(store, setupStore);
// 向pinia中放入store
pinia._s.set(id, store);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(pinia);
}, 2000);
};
const wrapAction = (key: string, action: any, store: any) => {
return (...args: Parameters<typeof action>) => {
// 触发action之前 可以触发一些额外的逻辑,这是actions除去Object.assign之外做的第二个处理📌
const res = Reflect.apply(action, store, args);
// 返回值也可以做处理
return res;
};
};
- 思路第5步:以上的分析都是针对optionStore(选项式定义),接下来看setUpStore(组合式定义)
function useStore() {
// 必须在setup中使用
const currentInstance = getCurrentInstance();
if (!currentInstance) throw new Error("pinia 需要在setup函数中使用");
// 注入 pinia
const pinia = inject<IRootPinia>(symbolPinia)!;
// 还没注册
if (!pinia._s.has(id)) {
if (isSetupStore) {
// 创建setupStore
createSetupStore(id, storeSetup, pinia);
} else {
// counter:state:{count:0}
createOptionsStore(id, options, pinia);
}
}
// 获取store
const store = pinia._s.get(id);
return store;
}
const createSetupStore = (id: string, setup: () => any, pinia: IRootPinia) => {
// 一个store 就是一个reactive对象
const store = reactive({});
// store单独的scope
let scope: EffectScope;
// scope可以停止所有的store 每个store也可以停止自己的
const setupStore = pinia._e.run(() => {
scope = effectScope();
return scope.run(() => setup());
//此setup就是createSetupStore第二个参数=>组合式定义传入的第二个参数
//这也是组合式定义最后要return的原因 为了底层拿到返回值📌
});
// 处理action的this问题
for (const key in setupStore) {
const prop = setupStore[key];
if (typeof prop === "function") {
// 扩展action
setupStore[key] = wrapAction(key, prop, store);
}
}
Object.assign(store, setupStore);
// 向pinia中放入store
pinia._s.set(id, store);
return store;
};
const createOptionsStore = (
id: string,
options: Pick<IPiniaStoreOptions, "actions" | "getters" | "state">,
pinia: IRootPinia
) => {
const { state, getters = {}, actions } = options;
const setup = () => {
// 缓存 state
if (pinia.state.value[id]) {
console.warn(`${id} store 已经存在!`);
}
const localState = (pinia.state.value[id] = state ? state() : {});
return Object.assign(
localState,
actions,
Object.keys(getters).reduce(
(computedGetter: { [key: string]: ComputedRef<any> }, name) => {
// 计算属性可缓存
computedGetter[name] = computed(() => {
// 我们需要获取当前的store是谁
return Reflect.apply(getters[name], store, [store]);
});
return computedGetter;
},
{}
)
);
};
const store = createSetupStore(id, setup, pinia);
//组合式定义中,并没有选项式对state、getters、actions的处理,因为选项式的底层就是组合式:
//此createOptionsStore调用的就是createSetupStore函数📌
};
四、VueClI使用和原理剖析
介绍
以下原理是前者的介绍,现在官方推荐create-vue
//VueCLI创建应用
npm install -g @vue/cli
vue create hello
//vue-create创建
npm create vue@3
原理
目的:探究命令背后做了什么。
总结:VueClI通过 PluginAPI(@vue/cli-service/lib/~) 实现了Service.js(@vue/cli-service/lib/~)和service.js(@vue/cli-service/lib/commands/~)的解耦和联动,即vueCLI如何实现插件机制。
实践:如果自己去写第三方库,也是要实现插件机制的。可以通过查看优秀的源码,学到一些思想。
- 思路:需补充
常用命令的使用
- serve
用法:vue-cli-service serve [options] [entry]
选项:
--open 在服务器启动时打开浏览器
--copy 在服务器启动时将 URL 复制到剪切版
--mode 指定环境模式 (默认值:development)
--host 指定 host (默认值:0.0.0.0)
--port 指定 port (默认值:8080)
--https 使用 https (默认值:false)
vue-cli-service serve 会启动一个开发服务器(基于 webpack-dev-server),并附带开箱即用的热快热重载(Hot-Module-Replacement).
除了通过命令行参数[entry],也可以使用vue.config.js里的 devServer字段配置开发服务器。
[entry]将会被指定为唯一入口(默认值src/main.js)。
build
inspect
help
五、VueCLI插件和Preset
VueCLI插件
当vueCLI无法满足开发需求,详见官网-插件开发指南
Preset
Preset就是一个json配置,
六、VueCLI配置
WARNING
Vue CLI 现已处于维护模式!
现在官方推荐使用 create-vue 来创建基于 Vite 的新项目。 另外请参考 Vue 3 工具链指南 以了解最新的工具推荐。
